
Bell’s Palsy
A 48 year old man presents with sudden onset weakness on the left side of his face and difficulty closing his left eye.

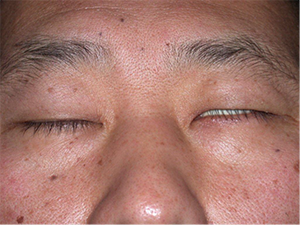
What is Bell’s Palsy?
Bell’s Palsy, also known as idiopathic facial paralysis, is a condition in which the muscles on one side of the face suddenly become weakened or paralyzed, causing half of the face to droop.
What causes Bell’s Palsy?
Bell’s Palsy occurs as a result of swelling or inflammation of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), the nerve that controls the facial muscles. The exact cause is not known, but it may occur after a viral infection or even associated with the virus that causes cold sores (Herpes Simplex) or shingles (Herpes Zoster). If the facial nerve is damaged as a result of trauma or surgery, it is more accurately described as a “facial nerve palsy” rather than “Bell’s Palsy.”
Who is at risk for Bell’s Palsy?
Bell’s Palsy can occur at any age, but pregnant women and diabetics may be at more risk.
What are the symptoms of Bell’s Palsy?
Because of the weakness of the muscles around the mouth, those affected may have difficulty with speech and drooling. Because of the weakness of the muscles that close the eyelids, the eye may become dry, red, painful, watery, and possibly ulcerated and infected.
Is Bell’s Palsy permanent?
Most cases resolve within a month. Some cases have a permanent residual weakness.
How is Bell’s Palsy treated?
Coticosteroids and antiviral drugs can be used. Surgical correction or BOTOX can help cases in which there is long term complications.
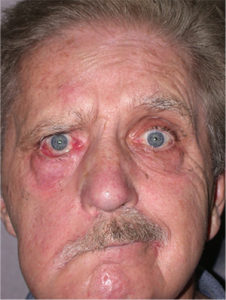
Right sided Bell’s Palsy. Note drooping of eyebrow, lower lid, and lower face.
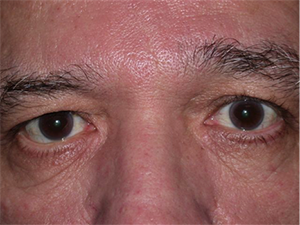
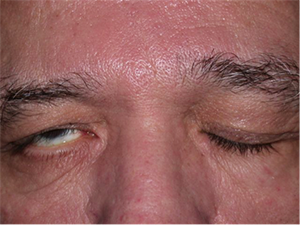
Right sided Bell’s Palsy. Note incomplete eyelid closure.
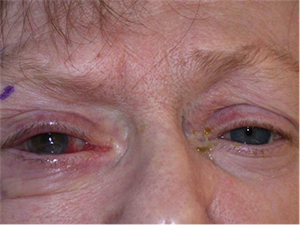
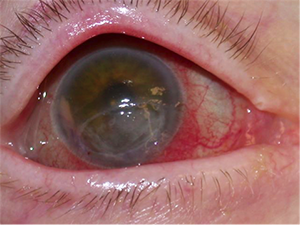
Right sided Bell’s Palsy. Corneal ulceration from poor eyelid closure.
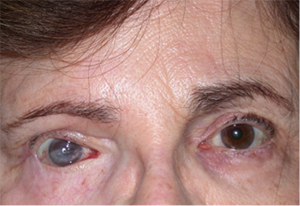
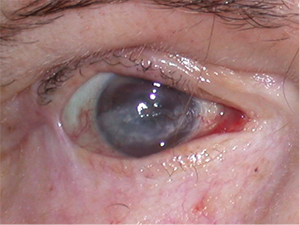
Right corneal scarring from Bell’s Palsy.
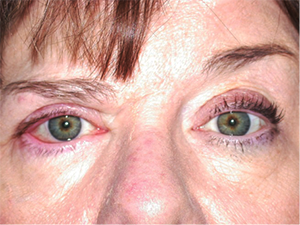
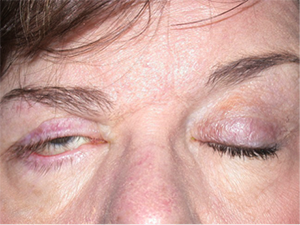
Right sided Bell’s Palsy with poor eyelid closure.
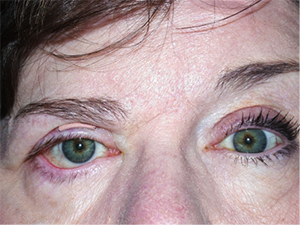
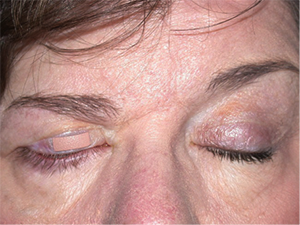
Same patient with placement of external right upper eyelid weight to improve closure.
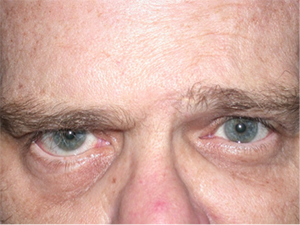
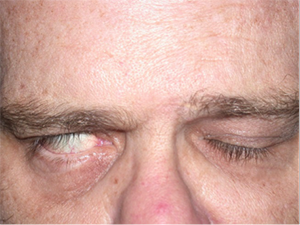
Right sided Bell’s palsy before surgical implantation of right upper eyelid weight.
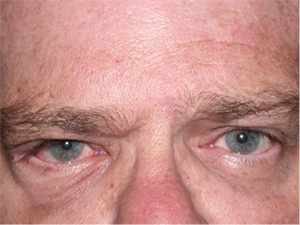
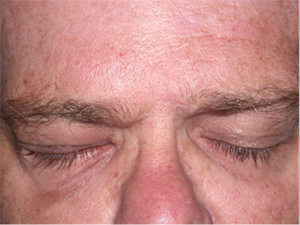
Same patient after surgical implantation of right upper eyelid weight.
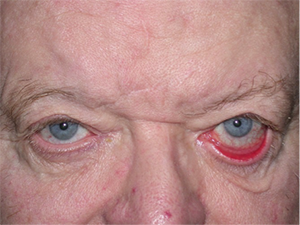
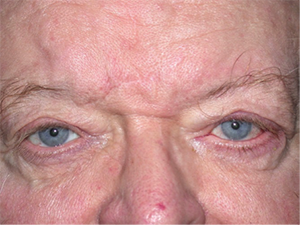
Left sided Bell’s Palsy before and after left lower eyelid surgery.
Recent Comments